
Why Every Website Needs an SSL Certificate
You land on a website, click the padlock icon, and feel relieved. That simple gesture often signals the difference between “just browsing” and “trusting with my data.” For business owners and marketing leaders, that small green icon isn’t just a matter of security; it’s a meaningful trust signal, a conversion driver, and an SEO boost. As a seasoned content writer for digital brands, you know this matters. So let’s dive into the world of SSL certificates and see how SSL works.
Definition and Basic Concept of SSL Certificates
When someone asks you for the SSL certificate meaning, keep it crisp: it’s a digital file issued to a website by a Certificate Authority that proves two things:
- The identity of the website.
- Information that the user wants with the server is protected.
- The certificate allows the change from “http://” to “https://”, which means the connection is encrypted and authenticated.
That question still remains- why HTTPS matters? The answer comes from the fact that website trust and security are the basis of the whole online ecosystem today, and cannot be compromised. The use of HTTPS by websites has already reached more than 88%.
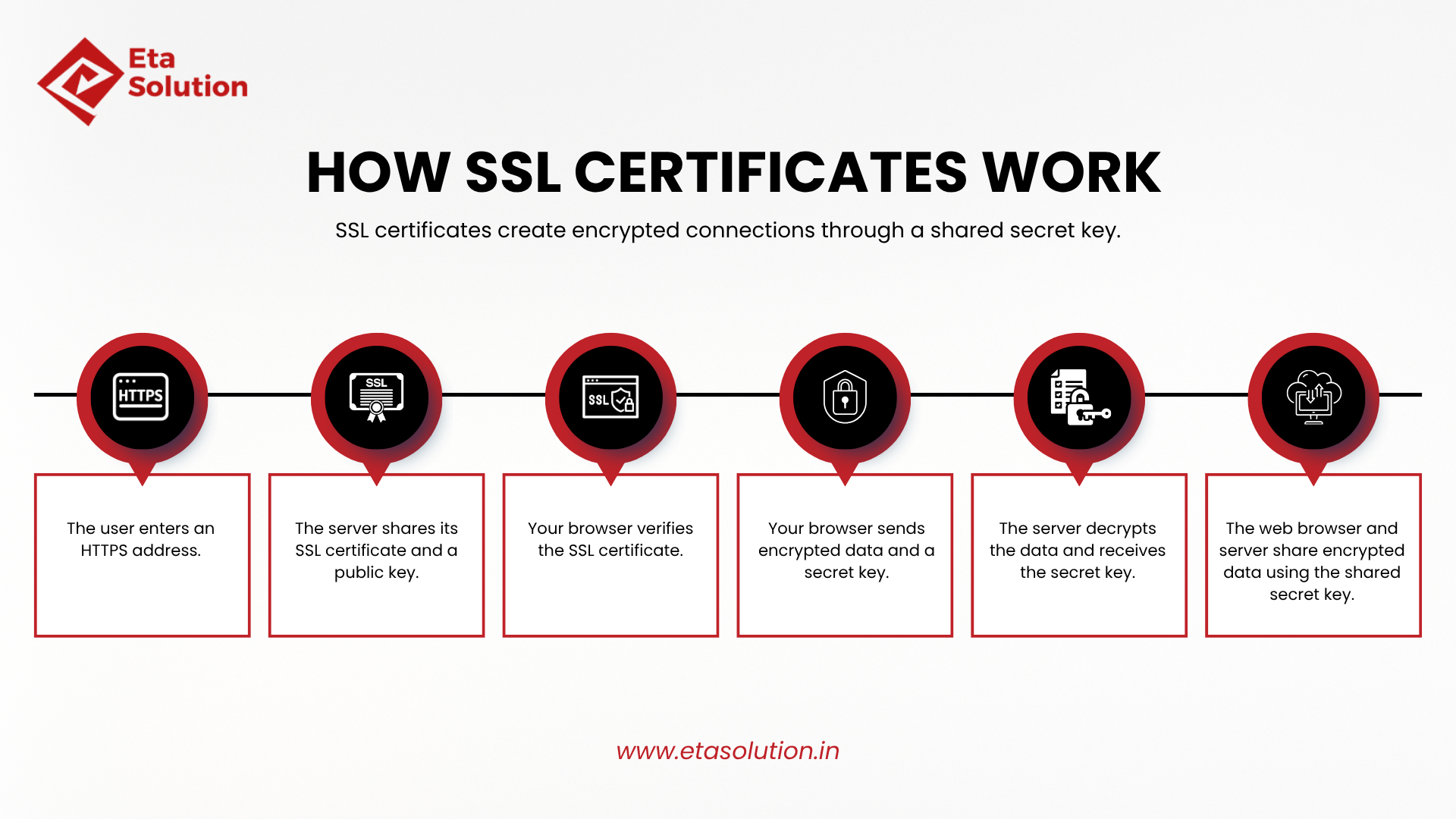
How SSL Certificates Work
Without too much technical jargon, business decision makers can understand from the description below the working principle of SSL.
- You get the certificate from a Certificate Authority.
- The CA checks your domain.
- The server that the certificate is for is the one where the certificate is set up, with the public key, the identity of the site, the issuer info, the expiry date, and the like etc.
- The browser of the user wants to establish a secure link: the “SSL handshake” occurs, the keys are handed over, checked, and encryption of the session starts.
- The data transmissions are done over HTTPS traffic and can ensure that it has not been tampered with.
- The browser will give a warning if the user is trying to access a site that has something wrong with it.
As a matter of fact, a bad configuration of your certificate can bring you into danger even if you have one.
Different Types of SSL Certificates Explained
That is to say, the differences that come with the various types of certificates are the main features that distinguish the major types and situations for the use of them:
- Domain Validated: Validates domain ownership only. Good for blogs or informational sites.
- Organization Validated: Validates the business entity as well as the domain. Ideal for brand websites collecting user data.
- Extended Validation: The highest-level trust certificate. Rigorous business checks, visible brand indicators in some browsers useful for eCommerce or financial sites.
Also note wildcard certificates and multi-domain certificates if you run complex sites.
Why SSL Is Essential for Website Security Certificate
You already know the “importance of SSL” is more than buzz. It’s about defending your brand and your users. Key points:
- Encryption for data protection online, so if someone intercepts the communication, they can’t read it.
- The certificate authenticates your site’s identity, reducing the risk of phishing or domain spoofing.
- Browsers now mark non-HTTPS pages as “Not secure”. That can erode user confidence before they even engage.
In 2023, about 32% of U.S. websites with SSL settings still scored an F due to poor configuration.
SSL for SEO Rankings
You know SEO, so here’s how SSL ties in with it in real terms:
- SSL vs TLS: The protocol shift to HTTPS security has become a subtle ranking factor. The major certificate providers note that TLS/SSL is now “standard” for SEO.
- Statistics: Browsing time across major browsers exceeded 93% on HTTPS pages.
- Practical takeaway: As you pitch for “best SEO company in Ahmedabad”, mention that your clients’ websites achieve better trust metrics, reduced bounce rate, and improved ranking long-term when secured with SSL benefits.
- Extra nuance: Search engines may weigh user experience signals.
- Secure website tips: losing “padlock” = losing micro-trust = possible traffic loss.
SSL Certificate and Website Trust: Building User Confidence
Trust isn’t just a word in a marketing deck; it’s something users sense. Consider:
- A user sees a padlock, checks for certificate details, and believes the brand is legit.
- A non-secure site often triggers a browser warning, raising doubt even before content loads.
A US retail brand re-negotiated its web theme to move ALL pages to HTTPS. They reported a 12% uplift in conversion rate users just stayed longer.
You, as someone positioning a brand, can frame it like: “When we partner with the best SEO company in Ahmedabad, we don’t just optimize content, we future-proof your site’s trust architecture.”
Some phishing sites use legitimate free SSL certificates to appear safe. In 2023, >90 % of phishing websites used HTTPS.
Impact of SSL on E-commerce and Online Payments
For businesses, especially those doing online sales, the SSL for eCommerce segment is mission-critical. Consider:
- Payment gateways often require HTTPS for integration. Without it, you may not even get certified.
- If the checkout page is “Not Secure”, drop-off risk skyrockets. One study found non-HTTPS checkout pages deter ~30% of users.
- For multi-region businesses, make sure your certificate covers all domains/sub-domains or you’ll trigger browser warnings mid-checkout.
- Expert view: At security seminars this year, several CISOs highlighted certificate expiry as one of the weakest links in eCommerce security operations. It’s not the lack of encryption; it’s the mismanagement of certificates that triggers real risk.
How to Install and Configure an SSL Certificate
Even if “install SSL certificate” isn’t your specialty, you should know the high-level steps and what to watch out for.
Steps:
- Decide on the kind of certificate you need and a reliable CA.
- Create a Certificate Signing Request on your server.
- CA verifies your request and sends you the certificate file.
- Put the certificate on your web server.
- Modify the web server settings so that HTTPS is used.
- Confirm the change by SSL tools online.
- Automate certificate renewal. Avoid relying on “remember to renew” – that’s human error waiting to happen.
If you’re partnering with the best SEO company in Ahmedabad, ask: “What’s our certificate renewal plan and who monitors the security chain for us?”
Common SSL Errors and How to Fix Them
No one likes surprises when a website displays “Your connection is not private”. Here are typical errors and how to address them:
- Expired certificate – set up monitoring/alerts → fix by renewing.
- Wrong domain name on certificate – ensure certificate matches the host or use SAN/wildcard.
- Mixed content warnings – your page is HTTPS but loads some HTTP assets. Update all links.
- Poor protocol/cipher suite – for instance, a site that continues to employ SSLv2 or SSLv3, both of which are considered unsafe. Ideally, you should be using TLS 1.2+.
- Chain/authority issues – that is to say, a missing intermediate certificate can still be the reason for warnings. Checking the chain with a tool is the best way to find out.
Not only is security maintained by you when being very close to these mistakes and changing them into points for fixes, but also trust and SEO parity.
Free vs Paid SSL Certificates: Which One Should You Choose?
It is a table that you can employ while giving the information to the clients.
Free certificates:
- Often, Domain Validated only.
- Shorter validity but renewable.
- Good for blogs, content sites, and low-risk pages.
Paid certificates:
- Provide OV/EV options.
- Often come with higher warranty, support, and brand indicators.
- Useful for eCommerce, large-brand trust context, and multi-domain deployments.
Which should you pick? For most marketing-led websites, the free option may be sufficient as long as it’s installed correctly and renewed. But if you’re a brand where trust and identity matter, go paid.
When you tell clients “We’re the Best SEO company in Ahmedabad for your brand”, you can add “We’ll guide you on which certificate type matches your business risk and trust posture”.
Final Take
It’s not really the case that a user coming to your website and seeing the secure padlock would instantly think “SSL certificate” right in those very words. What sticks is the security feeling. And I must say, for a business decision-maker or marketing expert, figuring out the mechanism and the reasons for SSL is a tool: SEO to trust and conversion to trust.
If you omit the certificate or put it only halfway during the installation, you are basically telling users to trust you, although you have one hand tied behind your back. On the other hand, when you set up and keep it in a proper way, it is like an unseen support of your brand. Therefore, the question for the team to think about is: How long ago have we checked our website encryption, certificate expiration, and configuration correctness?
As you craft your next campaign or client strategy, remember: it’s not just about traffic or keywords, it’s about the roof being secure before you throw the doors open.
Free SSL certificates such as Let’s Encrypt offer basic DV-level encryption, which is fine for personal blogs or non-commercial sites. However, businesses, eCommerce stores, and platforms handling sensitive user data should invest in paid SSL certificates. These come with higher validation levels, customer support, warranty coverage, and stronger security features, which enhance trust and protect users more effectively.
A website without SSL is flagged as “Not Secure” in browsers like Chrome and Safari. This scares users away and reduces engagement. Additionally, the website is vulnerable to cyberattacks, including data theft, session hijacking, and MITM attacks. Search engines also push insecure websites lower in rankings, affecting visibility and business growth. For any website collecting personal data, lack of SSL can also lead to legal complications.
Most SSL certificates are valid for one year. Renewing them on time is crucial because once an SSL expires, browsers immediately show security warnings to users, indicating that the site is unsafe. This can severely impact traffic, conversions, and brand image. Many site owners use auto-renewal to avoid downtime and ensure continuous encryption and trust signals.
Yes. SSL certificates come in different levels of validation and coverage:
DV (Domain Validation): Basic validation, ideal for blogs or simple sites.
OV (Organization Validation): Confirms the business identity, suitable for company websites.
EV (Extended Validation): Displays a green bar or company name in the browser for maximum trust—used by banks, enterprises, and eCommerce sites.
Wildcard SSL: Secures the main domain and unlimited subdomains.
Multi-domain SSL: Secures multiple domains under one certificate.
Absolutely. Google officially announced HTTPS as a ranking factor. Websites with SSL are considered safer and more reliable, which helps them rank better in search results. Furthermore, HTTPS improves overall site performance by enabling modern features like HTTP/2, which speeds up page loading. A secure site also reduces bounce rates since users feel safe browsing it—another indirect SEO benefit.

What started as a passion for marketing years ago turned into a purposeful journey of helping businesses communicate in a way that truly connects. I’m Heta Dave, the Founder & CEO of Eta Marketing Solution! With a sharp focus on strategy and human-first marketing, I closely work with brands to help them stand out of the crowd and create something that lasts, not just in visibility, but in impact!

How User Intent Drives Modern Search Strategies

20 Marketing KPIs to Track & Improve in 2026


