Google Shopping Made Easy | Complete Beginner’s Tutorial
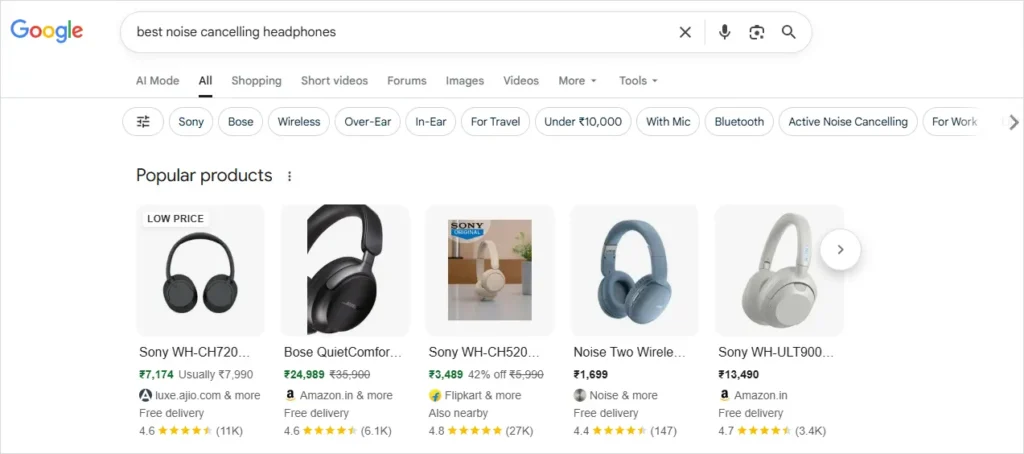
Suppose you do a Google search for the phrase “best noise cancelling headphones”. What you would actually get as a result would not be just a list of text links but rather a more informative and visually appealing presentation of product images, prices, and brand names arranged in a row. This is not other than Google Shopping activity. To the user, it feels seamless. But for businesses, it’s a high-stakes marketing arena where visibility, feed precision, and campaign strategy decide who wins the sale.
For business owners, marketing experts, and CEOs who already live in the digital world, Google Shopping is no longer optional. It’s central to how customers discover, compare, and purchase. This guide breaks down not only the basics but also the advanced nuances that insiders focus on: setup, optimization, real campaign stories, and the upcoming AI-driven future of Google Shopping.
What Is Google Shopping and Why It Commands Attention
Google Shopping, which is also known as product listing ads or Google Product Ads, essentially is not a keyword bidding system like in the case of traditional search ads. In order to allow customers to find their products, companies have to feed their products into the Google Merchant Center, and through an automated process, Google identifies the data with the queries of the users.
Why it matters today:
- Scale and reach. By 2025, more than 1.2 billion searches per month will happen via Google Shopping. It has become the first touchpoint for many customers exploring new products.
- Click dominance. Google Shopping Ads Tutorial captures around 85% of paid clicks across Google Ads, showing the clear preference users have for product-rich formats.
- Buyer intent. Searches like “compare prices” have grown by 22% in 2025 alone, proving that shoppers use Google Shopping to move from browsing to buying.
- Discovery power. Around 70% of online shoppers say they’ve discovered a new brand through Google Shopping.
For brands and agencies alike, ignoring this platform is like ignoring the busiest shopping street in the city. It’s where product discovery meets purchase intent in its purest form.
The Foundation: Google Shopping Setup
1. Merchant Center + Product Feed
The Merchant Center is your gateway into Google Shopping. Think of it as the filing system where every product detail lives. A sloppy feed means your ads don’t show, or worse, they show incorrectly.
That’s why marketers pay close attention to feed attributes. Beyond the basics title, description, and price, you should enrich your feed with elements like GTINs, SKUs, availability, and even custom labels. These labels are underutilized but powerful: they let you categorize products by margin, seasonality, or inventory level so you can structure campaigns intelligently.
Brands that ignore feed optimization often see rejections or poor impressions. A recent Adsmurai study showed a 40% drop in rejected listings simply by restructuring the product feed. That’s not just compliance, it’s profit saved.
2. Linking Merchant Center to Google Ads
After you have made your feed live, the subsequent step is linking your Google Ads account with Merchant Center. By making this link, you can use the product data feed to create Google Shopping campaigns, where your feed automatically advertises for the matching search queries. What is the key difference from search campaigns? You don’t bid on keywords directly. Google decides which queries trigger your ads based on your product data. That makes your feed not just a technical requirement, but your primary marketing asset.
Structuring Google Shopping Campaigns the Smart Way
Getting approved is step one. Structuring campaigns for control and ROI is step two. Most seasoned marketers use a tiered architecture:
- High-priority campaigns are reserved for your best sellers or high-margin items where you’re willing to bid aggressively. This ensures your flagship products dominate.
- Mid-tier campaigns cover your core catalog. Here, bids are moderate, balancing exposure and profitability.
- Low-priority campaigns act as a catch-all, capturing long-tail or clearance products with lighter spend.
Why this works: It prevents Google from blindly serving your ads for every query. Instead, you direct spend where it makes sense.
Bidding also requires a Google Shopping strategy. While automated bidding like Target ROAS or Maximize Conversion Value is popular, it can backfire if margins vary across products. That’s why many agencies now shift to profit-based bidding (POAS), where margin data informs bids. This method ensures you’re not chasing revenue at the cost of profitability.
And don’t forget the invisible work: negative keywords and search term exclusions. Without them, your ads may appear for irrelevant queries, burning budget on clicks that will never convert.
Beyond Basics: Advanced Shopping Campaign Optimization
Once campaigns are running, the next challenge is scaling without losing efficiency. This is where shopping campaign optimization separates good accounts from great ones.
1. Profit-Based Bidding (POAS)
ROAS tells you revenue per ad dollar, but ignores costs like shipping or storage. By labeling products with profit margins, you can build campaigns that optimize for actual profit. DataFeedWatch shared a case where applying POAS lifted conversions by nearly 96% while improving ROAS.
2. Smart Segmentation
Seasonal or clearance products often need different treatment than evergreen items. By segmenting SKUs, you can run time-bound promotions without disrupting long-term campaigns. Many marketers also keep a “test” campaign to trial new products before committing larger budgets.
3. Dynamic Remarketing & Customer Match
Imagine a shopper clicks your ad for running shoes, browses your site, but doesn’t buy. With dynamic remarketing, they’ll later see the exact shoe in another Google placement—nudging them back to purchase. Paired with Customer Match, you can retarget existing customer lists with tailored promotions, making Shopping ads a full-funnel strategy.
4. Monitoring Search Terms
Shopping campaigns thrive on data. By studying which queries trigger your ads, you can refine product titles or add negatives. For instance, if your high-end “leather briefcase” keeps showing up for “cheap bags,” it’s time to adjust feed data or add exclusions.
5. Leveraging Automation
Scripts and APIs aren’t just for big players anymore. Smaller agencies now use simple rules to pause products with low CTRs, increase bids on items above ROAS thresholds to save time and protect budgets.
Real-World Stories That Prove the Model
Case 1: Code1Supply’s 5× ROAS Turnaround
This U.S.-based medical supply store struggled with poor feed quality and misfiring tags. By cleaning up their Merchant Center, fixing conversion tracking, and segmenting SKUs into campaigns, they turned performance around with a 5× ROAS. It wasn’t a huge budget increase; it was smart restructuring that paid off.
Case 2: DataFeedWatch Campaign Gains
In Europe, an agency applied profit-based segmentation and feed enrichments for an eCommerce client. The results speak volumes: nearly 96% more conversions, a 29% ROAS increase, and a 139% jump in conversion value. These numbers underline a key truth: Google Shopping rewards precision more than raw budget.
Trends & Future You Didn’t See Coming
1. Virtual Try-On & AI Shopping Agents
Google is piloting features that let users virtually try on clothes by uploading photos. Combined with AI “shopping agents” that can monitor prices and auto-complete purchases, the shopping journey is becoming more automated. For merchants, this means one thing: only precise, richly tagged feeds will survive algorithmic curation.
2. Conversational Search with Gemini
Google’s “AI Mode” is rolling out, where shoppers can ask conversational queries like “show me waterproof backpacks for my Portland trip in April.” Product listing Google Ads will be selected based on semantic clarity in descriptions, not just raw keywords. Businesses need to start writing product titles and descriptions for both humans and AI crawlers.
3. Behavior Trends
- Mobile is the most powerful channel: more than 70% of Shopping ad clicks have been from mobile devices.
- The way people find products is changing: 33% of product discovery online is done straight from Google Shopping guide, which has become the leading channel for brand-free search.
- Users are becoming more sensitive to prices: a larger number of shoppers are using Shopping for comparison of prices given live, which is making brands set prices more competitively.
Such trends do not represent distant phenomena anymore; they are the indicators of the next competition arena.
The Takeaway: Elevate Your Ecommerce Digital Marketing Services with Google Shopping
Google Shopping is more than just a channel; it’s a strategy platform. It blends feed management, campaign architecture, bidding science, and consumer psychology. For agencies offering Ecommerce digital marketing services, Shopping mastery is now a benchmark of expertise.
The formula is clear:
- Build feeds that are clean, complete, and dynamic.
- Segment campaigns smartly with priority tiers.
- Try using profit-conscious bidding to keep your profits safe.
- Utilize the full potential of the machine but still keep human control.
- Get ready for AI-powered shopping agents that will change consumers’ interaction with product listings.
The question still remains: will your product feeds be able to contend in a future in which artificial intelligence, rather than a shopper, will decide what gets the closest look?
Once you upload your product data to Google Merchant Center, it typically takes 24 to 72 hours for your listings to appear on Google Shopping, provided everything meets Google’s requirements. During this time, Google reviews your feed to ensure your products comply with its policies, have accurate pricing, and include valid URLs and images. If there are any errors or disapprovals, your listings may be delayed until those issues are resolved. To speed up the process, make sure your product feed is complete, up-to-date, and correctly formatted before submission.
Optimizing your Google Shopping ads involves improving both your product data quality and campaign performance strategy. Start by writing clear and keyword-rich product titles and descriptions that match user search intent. Use high-resolution images and ensure prices, availability, and shipping details are accurate. Next, regularly review your campaign performance in Google Ads—adjust bids based on profitable products, use negative keywords to filter irrelevant traffic, and segment campaigns by product category or brand. Continuous monitoring and testing help improve click-through rates (CTR) and return on ad spend (ROAS).
A Google Merchant Center feed is a structured file that contains all your product information—such as titles, prices, images, descriptions, availability, and unique product identifiers (like GTINs). This feed acts as the foundation for your Google Shopping campaigns, as it tells Google exactly what products you’re selling and how to display them in search results. You can create your feed manually (via spreadsheet), use an eCommerce platform integration (like Shopify or WooCommerce), or automate it through your website’s product catalog. Keeping your feed accurate and updated is essential to ensure your listings remain active and compliant.
Google Shopping helps eCommerce businesses by increasing visibility, driving targeted traffic, and boosting sales conversions. When potential buyers search for products similar to yours, Google Shopping displays your listings with images, prices, and store names—right at the top of search results. This visual and informative presentation helps shoppers compare options instantly, leading to higher engagement and qualified clicks. Additionally, businesses can leverage performance data to understand customer behavior, refine pricing strategies, and improve product performance over time.
To list products on Google Shopping, you must first create a Google Merchant Center account and ensure your website meets Google’s shopping policies. Your product listings must include essential details such as accurate titles, descriptions, images, pricing, and availability. You’ll also need to provide a valid product feed, adhere to content guidelines (e.g., no misleading or restricted products), and use HTTPS for secure checkout. It’s also important that your store has clear refund, shipping, and contact information to establish trust and comply with Google’s listing standards.

What started as a passion for marketing years ago turned into a purposeful journey of helping businesses communicate in a way that truly connects. I’m Heta Dave, the Founder & CEO of Eta Marketing Solution! With a sharp focus on strategy and human-first marketing, I closely work with brands to help them stand out of the crowd and create something that lasts, not just in visibility, but in impact!

DO’s and DON’Ts on Google My Business

How to Resolve Duplicate Content

How to Align Sales & Marketing in Industrial Businesses

